Protocol - Blood Pressure (Adult/Primary)
- Alcohol - Lifetime Use Disorder
- Cigarette Smoking Status - Adolescent
- Cigarette Smoking Status - Adult
- Height - Knee Height
- Height - Recumbent Length
- Height - Self-Reported Height
- Height - Standing Height
- Lipid Profile
- Waist Circumference - Framingham Heart Study
- Waist Circumference - Waist Circumference NCFS
- Waist Circumference - Waist Circumference NHANES
- Weight - Measured Weight
- Weight - Self-Reported Weight
Description
A measure to assess a respondents systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which is used to determine high blood pressure (hypertension). Assessment must also include measures for personal history of high blood pressure and a history of medication usage.
Specific Instructions
Ask questions "1" and "2," and then proceed to the protocol for obtaining blood pressure. The use of high blood pressure medications must be obtained.
The Sickle Cell Disease Curative Therapies Working Group notes that definitions of blood pressure categories (normal, elevated, stage 1 hypertension, and stage 2 hypertension) for children are included in table 3 of Flynn et al., 2017 (see General References).
Availability
This protocol is freely available; permission not required for use.
Protocol
1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have:
High blood pressure or hypertension?
[ ] 1 No
[ ] 2 Yes
[ ] 8 Not Sure
If Yes:
At what age were you first told this? __ __
FOR WOMEN: Was this during pregnancy only?
[ ] 1 No
[ ] 2 Yes
2. Have you ever taken medication for hypertension/high blood pressure?
[ ] 0 no
[ ] 1 yes, now
[ ] 2 yes, not now
[ ] 9 unknown
If yes, then…
At what age did you begin taking medicine for this? __ __
[ ] 99 unknown
3. BLOOD PRESSURE METHODS
This protocol, which was taken from the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study, is written for use with the Omron® HEM907XL automated BP monitor. Special attention must be placed on assessment and maintenance of the instruments accuracy as per the manual that accompanies the instrument.
The design and operation of the Omron® HEM907XL are based upon the combined principles of compression of the brachial artery under an elastic, inflatable cuff and estimation of the systolic and diastolic BP levels by oscillimetric methods. The technician should place the correct size cuff on the participants arm, set the machine to automatic, set the mode button to single, and push the start button on the monitor, then wait for the output. All readings are to be recorded to the nearest digit.
3.1. Measurement Equipment
The following equipment will be required for BP and pulse measurement:
a. One Omron® HEM907XL automated BP monitor.
b. BP cuffs in four sizes: S, M, L, XL
c. One standard clinical mercury sphygmomanometer*
d. One clinical thigh cuff*
e. One Gulick II tape (or Gulick II Plus)
f. A chair with arm support for BP measurement, or a chair and table (table must provide for a comfortable resting posture of the arm with the cubital fossa at the level of the 4th intercostal space at heart level)
g. Form for recording BP and pulse
h. One black pen (marking on skin) and one No. 2 pencil (completing the form)
* used for arms >50 cm in circumference
3.2. Cuff Size Determination
The proper cuff size must be used to avoid under- or over-estimation of BP. Cuff size refers to the cuffs bladder, not the cloth. A copy of the chart below should be attached to the sphygmomanometer for easy reference. In addition, the cuffs must be HEM907 XL-compatible.
a. Cuff Size Indicated by Measured Arm Circumference
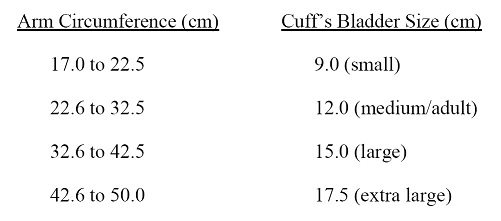
b. Measurement of arm circumference. The participant should remove his/her upper garment, or clear the upper arm area so that an unencumbered measurement may be made. The technician should:
i. Have the participant stand, with the right arm hanging and bending the elbow so that the forearm is horizontal (parallel) to the floor.
ii. Measure arm length from the acromion (bony protuberance at the shoulder) to the olecranon (tip of the elbow), using the Gulick II anthropometric tape.
iii. Mark the midpoint on the dorsal surface of the arm.
iv. Have the participant relax arm along side of the body.
v. Draw the tape snugly around the arm at the midpoint mark.
NOTE: Tape should be horizontal and should not indent the skin.
vi. Noting the arm circumference indicated by the tape, use the criteria above for determining cuff size.
3.3. Wrapping the Blood Pressure Cuff Around the Arm
The technician should:
a. Ensure the participant is seated, legs uncrossed, in a quiet room, with the elbow and forearm resting comfortably on the armrest of the BP measurement chair (or table), with the palm of the hand turned upward. The area to which the cuff is to be applied must be bare (free of clothing).
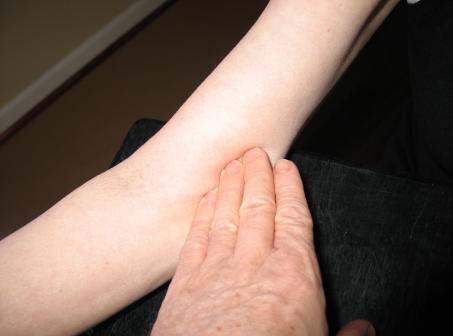
b. Locate the brachial artery by palpation and mark the skin with a small dot, using a black pen. (The brachial artery is usually found just medial and superior to the cubital fossa, posterior to the biceps muscle and slightly toward the body.) For brachial artery palpation, fingertips or thumb may be used (see figure below).
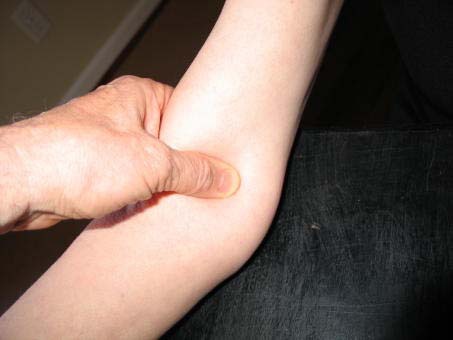
c. Place the appropriate cuff around the upper right arm so that:
i. The midpoint of the length of the bladder lies over the brachial artery.
ii. The cubital fossa is at heart level.
NOTE: The midpoint of the length of the bladder should be confirmed by folding the bladder in two. The marking on the cuff should not be trusted.
d. Place the lower edge of the cuff, with its tubing connections, about 1 inch above the natural crease across the inner aspect of the elbow (the cubital fossa).
e. Wrap the cuff snugly about the arm, with the palm of the participants hand turned upward, making sure the long edges of the cuff lie on top of each other as the cuff is wrapped around.
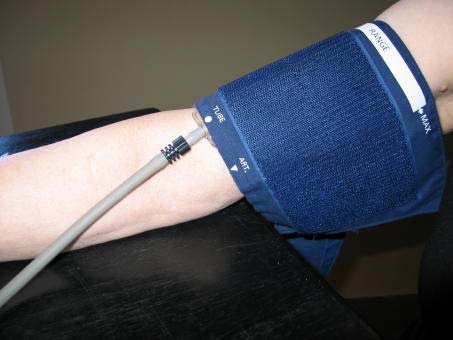
f. Secure the wrapped cuff firmly by applying pressure to the locking fabric fastener over the area where it is applied to the cuff.
NOTE: The cuff should not be wrapped too tightly around the arm.
NOTE: If a thigh cuff is needed, the standard mercury sphygmomanometer is used to measure the BP systolic and diastolic pressures at the disappearance of Korotkoff sounds.
3.4. Setting the Mode and P-Set
The technician should:
a. Check that the AC adaptor is attached to the monitor and plug into electrical outlet.

b. Turn the ON/OFF button to ON.
c. Set the MODE selector to SINGLE.

d. Set the P-SET (inflation level) knob to AUTO.

e. Connect the air:
i. For cuff sizes small, medium and large, connect the air tube to the main unit by attaching the air plug to the base of the air connector.
ii. The extra large cuff has an air plug already connected. Attach this to the base of the monitor at the air connector.

3.5. Taking the First Blood Pressure Measurement
The technician should:
a. Have the participant sit quietly for a period of five minutes before the first BP is taken.
b. Push the START button on the monitor and wait for the output.
c. Record the systolic and diastolic BPs.
3.6. Taking the Second and Third Blood Pressure Measurements
The technician should:
a. Hold the participants arm vertical (without fist-clenching) for a full five seconds between each measurement
b. Wait 25 to 30 seconds between each measurement.
c. Repeat the steps described above to obtain the second and third BPs.
d. Record the systolic and diastolic BP.
Note: Omron® IntelliSense™ Blood Pressure Monitor Model HEM907XL is a registered trademark of OMRON Corporation
Diagnostic Criteria:
Hypertension in adults aged 18 years and older is defined by recorded blood pressures at or above an average of 140 mmHg systolic or 90 mmHg diastolic on two or more seated blood pressures, measured properly with well maintained equipment, at two or more visits to the office or clinic, or the prescription of one or more antihypertensive drugs for the purpose of blood pressure control. A diagnosis of prehypertension may also be used for similarly measured blood pressures with systolic pressures 120-139 mmHg or diastolic pressures of 80-89 mmHg when antihypertensive treatments are not taken.
This chart provides current diagnostic criteria as of August 2009.
| Systolic | Diastolic | |
| Normal | <120 mm Hg | <80 mm Hg |
| Prehypertension | 120-139 mm Hg | <80 mm Hg |
| Hypertension Stage 1 | 130-139 mm Hg | 80-89 mm Hg |
| Hypertension Stage 2 | >140 mm Hg | >90 mm Hg |
Personnel and Training Required
Trained and certified technicians to take blood pressures.
Equipment Needs
One Omron® HEM907XL automated blood pressure (BP) monitor, BP cuffs in four sizes: S, M, L, XL; one standard clinical mercury sphygmomanometer*; one clinical thigh cuff*; one Gulick II tape (or Gulick II Plus); a chair with arm support for BP measurement, or a chair and table (table must provide for a comfortable resting posture of the arm with the cubital fossa at the level of the 4th intercostal space at heart level).
*Used for arms >50 cm in circumference
Researchers should ensure that the equipment they use has been validated and that they follow the manufacturers guidelines for administration and calibration. The three most widely used validation protocols are the British Hypertension Society (BHS) Protocol; the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) Standard; and, more recently, the International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension (IP).
Note: Manufacturers of blood pressure equipment frequently make improvements and update both their equipment and software with the latest technological advances. The recommended equipment for this protocol in PhenX is current as of July 2009. Please refer to the specifications for your model number to ensure the level of information collected is compatible with the PhenX protocol.
Requirements
| Requirement Category | Required |
|---|---|
| Major equipment | No |
| Specialized training | Yes |
| Specialized requirements for biospecimen collection | No |
| Average time of greater than 15 minutes in an unaffected individual | No |
Mode of Administration
Interviewer-administered question, Clinical measurement
Lifestage
Adult
Participants
Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study: ≥18 years old
Framingham Heart Study (FHS): ages 19–79 years old
Note: The Working Group suggests that the same methodology be used for men and women of any age.
Selection Rationale
The first two protocols were selected because together they obtain a personal history of high blood pressure or hypertension as well as medication usage. These two pieces are a vital component in interpreting the results of a blood pressure measurement. Additionally, both protocols were used on a major U.S. health study. The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study protocol for measuring blood pressure was selected because of its use of the Omron® machine, which is the latest technology for measuring blood pressure. Conducting a blood pressure measurement provides additional study specificity.
Language
Chinese, English, Other languages available at source
Standards
| Standard | Name | ID | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) | Blood pressure proto | 62392-6 | LOINC |
| Human Phenotype Ontology | Abnormal systemic blood pressure | HP:0030972 | HPO |
| caDSR Form | PhenX PX040301 - Blood Pressure Adult Primary | 5822494 | caDSR Form |
Derived Variables
None
Process and Review
Not applicable.
Protocol Name from Source
Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA), Y20 CARDIA VII & Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Generation 3
Source
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Y20 CARDIA VII. Medical History Form. Page 1. Question 1 (source for question 1).
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and Boston University. Framingham Heart Study (FHS). Generation 3. Exam 1. Medical History—Medications. Page 23. No question number provided (source for question 2).
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Year 20 (2005–2006) Manual of Operations. Section 3—Blood Pressure and Pulse (source for question 3).
Reboussin, D. M., Allen, N. B., Griswold, M. E., Guallar, E., Hong, Y., Lackland, D. T., Miller, E., 3rd, Polonsky, T., Thompson-Paul, A. M., & Vupputuri, S. (2018). Systematic Review for the 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation, 138(17), e595-e616.General References
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. American National Standard. Manual, electronic or automated sphygmomanometers ANSI/AAMI SP10-2002/A1. 3330 Washington Boulevard, Suite 400, Arlington, VA 22201-4598, USA: AAMI; 2003.
Flynn, J. T., Kaelber, D. C., Baker-Smith, C. M., Blowey, D., Carroll, A. E., Daniels, S. R., de Ferranti, S. D., Dionne, J. M., Falkner, B., Flinn, S. K., Gidding, S. S., Goodwin, C., Leu, M. G., Powers, M. E., Rea, C., Samuels, J., Simasek, M., Thaker, V. V., Urbina, E. M., & SUBCOMMITTEE ON SCREENING AND MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN CHILDREN (2017). Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics, 140(3), e20171904
OBrien, E., Petrie, J., Littler, W. A., de Swiet, M., Padfield, P. L., Altman, D., Bland, M., Coats, A., & Atkins, N. (1993). The British Hypertension Society protocol for the evaluation of blood pressure measuring devices. Journal of Hypertension, 11(2), S43–S62.
OBrien, E., Pickering, T., Asmar, R., Myers, M., Parati, G., Staessen, J., Mengden, T., Imai, Y., Waeber, B., Palatini, P., Atkins, N., & Gerin, W.; the Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring of the European Society of Hypertension. (2002). International protocol for validation of blood pressure measuring devices in adults. Blood Pressure Monitoring, 7, 3–17. Retrieved on July 21, 2009, from http://www.dableducational.org/pdfs/International%20Protocol%202002.pdf
Protocol ID
40301
Variables
Export Variables| Variable Name | Variable ID | Variable Description | dbGaP Mapping | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PX040301_Age_Have_High_Blood_Pressure | ||||
| PX040301010200 | At what age were you first told this? | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_Age_Take_HBP_Medication | ||||
| PX040301020200 | At what age did you begin taking medicine more | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Age_Take_HBP_Medication_Coded | ||||
| PX040301020201 | At what age did you begin taking medicine more | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Blood_Pressure_Measurement_Date | ||||
| PX040301030900 | Date of measurement of blood pressure. | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Cuff_Size | ||||
| PX040301030200 | Blood pressure measurement, cuff size. | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_Diastolic_Blood_Pressure_1 | ||||
| PX040301030400 | Diastolic Pressure measurement 1 (mm Hg). | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_Diastolic_Blood_Pressure_2 | ||||
| PX040301030600 | Diastolic Pressure measurement 2 (mm Hg). | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Diastolic_Blood_Pressure_3 | ||||
| PX040301030800 | Diastolic Pressure measurement 3 (mm Hg). | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Ever_Have_High_Blood_Pressure | ||||
| PX040301010100 | Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you more | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_Ever_Take_HBP_Medication | ||||
| PX040301020100 | Have you ever taken medication for more | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_HBP_During_Pregnancy_Only | ||||
| PX040301010300 | Was this during pregnancy only? | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Sphygmomanometer | ||||
| PX040301030100 | Blood pressure measurement, sphygmomanometer more | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Systolic_Blood_Pressure_1 | ||||
| PX040301030300 | Systolic Pressure measurement 1 (mm Hg). | Variable Mapping | ||
| PX040301_Systolic_Blood_Pressure_2 | ||||
| PX040301030500 | Systolic Pressure measurement 2 (mm Hg). | N/A | ||
| PX040301_Systolic_Blood_Pressure_3 | ||||
| PX040301030700 | Systolic Pressure measurement 3 (mm Hg). | N/A | ||
Measure Name
Blood Pressure (Adult/Primary)
Release Date
September 9, 2009
Definition
Measure to assess respondent's blood pressure.
Purpose
Blood pressure is used to assess the risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and kidney failure.
Keywords
Blood pressure, BP, hypertension, systolic, diastolic, personal history, metabolic syndrome, Cardiovascular, Heart attack, stroke, heart failure, kidney failure, hypertension, Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults, CARDIA, Framingham Heart Study, FHS, British Hypertension Society, BHS, Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, AAMI, International Protocol of the European Society of Hypertension
Measure Protocols
| Protocol ID | Protocol Name |
|---|---|
| 40301 | Blood Pressure (Adult/Primary) |