Protocol - Dental Caries Experience - Prevalence
Description
The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth Surfaces (DMFS) Index is used by a dentist or dental hygienist to determine the prevalence of coronal caries in permanent and primary teeth through an examination that records the three components.
Specific Instructions
Note from PhenX Oral Health Working Group (WG): The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) uses a web-based system for data entry that will beep and a message will be displayed in the lower right portion of the screen if two entries are made or a nonallowable entry is made. Data entry is prohibited until an allowable response is entered. There are laptop programs that can be used with this protocol, and the Oral Health WG recommends such a system as it does notify the recorder of correctable errors. An example of a paper data recording form is included as part of this protocol so that the user can see the format of such a data entry system. It also is good to have paper forms on hand in case of an electrical failure or some other problem that prohibits use of the electronic data entry system.
Availability
This protocol is freely available; permission not required for use.
Protocol
Decayed Tooth Surfaces (the D Component of the DMFS Index)
Frank lesions are detected as gross cavitation and thus present few problems in diagnosis. Incipient lesions captured in this survey, on the other hand, are more difficult to diagnose consistently. Incipient lesions may be subdivided into three categories according to location, each with the following special diagnostic considerations:
1. Pits and fissures on occlusal, facial, and lingual surfaces
These areas are classified as carious when the explorer catches after insertion with moderate, firm pressure, accompanied by either a softness at the base of the area and/or an opacity adjacent or the area providing evidence of undermining or demineralization. In other words, a deep pit or fissure in which the explorer catches is not sufficient evidence of decay without one or both of the following:
- Softness at the base of the area;
- Opacity adjacent to the area providing evidence of undermining or demineralization.
2. Smooth areas on facial (labial or buccal) or lingual surfaces
These areas are carious if they are (1) either decalcified or if there is a white spot as evidence of subsurface demineralization and (2) if the area is found to be soft by:
- Penetration with the explorer, or
- Scraping the area with the explorer.
Visual evidence of demineralization is not enough to diagnose caries.
3. Proximal surfaces
- When areas are accessible to direct visual and tactile examination, i.e., when there is no adjacent tooth, the same criteria is used for smooth area on facial or lingual surfaces..
- When areas are not available for direct examination, other criteria must be applied.
- On anterior teeth, trans-illumination can serve as a useful aid in discovering proximal lesions. Trans-illumination is achieved by placing a mirror lingually and positioning the examining light so that it passes through the teeth and reflects into the mirror. If a characteristic shadow or loss of translucency is seen on the proximal surface, then this is indicative of caries on the surface. Ideally, the actual diagnosis should be confirmed by detecting a break in the enamel surface with the explorer; however, clear visualization of a lesion by trans-illumination can justify a positive diagnosis.
- On posterior teeth, however, visual evidence alone, such as undermining under a marginal ridge, is not sufficient proof for diagnosing a proximal lesion. A positive diagnosis is made only if a break in the enamel surface can be detected with the explorer.
Missing Teeth (the M Component of the DMFS Index)
This criterion traditionally represented permanent teeth extracted only as a result of caries. However, because of the difficulty of correctly distinguishing between teeth extracted due to caries and those extracted for periodontal reasons, no attempt is made at the time of the examination to differentiate between these two causes of tooth loss. It is essential, however, to distinguish between teeth extracted because of caries or periodontal disease and those extracted or missing for other reasons.
- The code “E” is used to indicate teeth extracted because of caries or periodontal disease,
- The code “M” is used for teeth missing due to trauma, orthodontic treatment, or other non-disease-related causes.
- The code “U” is used to identify unerupted or congenitally missing teeth.
In order to determine whether an “E,” “M,” or “U” is called, the examiner will ask the Sample Person (SP) about the reason for tooth loss. Separate codes are used when a missing tooth has been replaced by a fixed or removable prosthesis.
- “R” is usedto designate a tooth that is missing due to dental disease, but has been replaced by a fixed restoration.
- “P” is used to designate a tooth that is missing due to dental disease, but has been replaced by a removable restoration.
- “X” is used to designate a tooth that is missing due to other causes, but has been replaced by a fixed restoration.
- “Q” is used to designate a tooth that is missing due to other causes, but has been replaced by a removable restoration.
A fixed or removable prosthetic replacement is considered to exist when it is visible in the mouth. If an appliance is not visible, the examiner should ask the SP if one exists. If the SP reports the existence of a removable appliance, the replacement is considered to exist if the SP reports he/she wears the appliance, no matter how infrequently.
When a replacement exists, the examiner does not consider its condition or adequacy when making the call. When a replacement does not exist, the examiner does not attempt a clinical judgment of the need or adequacy of space for a replacement, even if tooth movement has closed the space.
When more than one tooth has been replaced by a single pontic, each tooth space is scored as replaced.
| Not Replaced | Replaced | |
Disease | E | R, P |
Nondisease | M | X, Q |
When an implant is identified in Tooth Count, a code of “3,” the appropriate restorative codes for Coronal Caries would either be “R,” “X,” “P,” or “Q.” The correct code is based on restorative replacement type and the self-reported reasons for permanent tooth loss.
Filled Tooth Surfaces (the F component of the DMFS Index)
The F component represents a tooth surface that has been filled with either a permanent or a temporary as a result of caries. It is necessary to distinguish between surfaces restored because of caries and those restored for other reasons, such as trauma, hypoplasia, malformation, or bridge abutment. The examiner may question the SP as necessary to make the correct call.
Scoring Permanent Teeth
Sound permanent teeth (“S”) are distinguished from permanent teeth with restorations or caries (“Z”). The “Z” code precedes any other legitimate diagnostic call for decayed or filled surfaces. For example, if a permanent molar has occlusal caries and is otherwise sound, the “Z” code is combined with the code for occlusal caries, i.e., “Z1.” If the permanent tooth is sound, the “S” code is used alone. For permanent teeth coded as a “5” in the tooth count, the “T” or “J” codes must be used. Electronic data entry systems should not accept any other coronal caries codes.
Any permanent root tip that has had a replacement made for the appropriate coronal structure or serves as a supporting structure for an overdenture will be coded as a “T.” This includes visible residual roots present under any type of removable complete or partial denture. If a visible residual root is present and no replacement has been made, the correct code will be a “J.”
The specific codes for permanent teeth are listed below:
S = Sound permanent tooth (no decay or filing on any surface)
Z = Permanent tooth with surface condition
J = Permanent root tip is present but no restorative replacement is present
T = Permanent root tip is present but a restorative replacement is present
Scoring Primary Teeth
Decayed or filled surfaces of primary teeth are scored in the same manner as permanent teeth, using the same diagnostic criteria. However, because this survey Is concerned with both primary and permanent teeth, it is necessary to call sound primary teeth with a “deciduous” scope (“D”) to distinguish them from sound permanent teeth (“S”). The “K” code is used for primary teeth with restorations or caries to distinguish them from permanent teeth with restoration or caries (“Z). The “K” code precedes any other legitimate diagnostic call for decayed or filled surfaces on primary teeth. For example, if a primary molar has occlusal caries and is otherwise sound, the “K” code is combined with the code for occlusal caries (i.e., “K1”). If the primary tooth is sound, the “D” code is used alone.
Missing primary teeth present potential problems in scoring because it is often not possible to distinguish exfoliated teeth from those extracted due to caries, especially during the period of mixed dentition. To avoid this problem, at the time of examination, all missing primary teeth are scored as unerupted permanent teeth (“U”). When data are analyzed, the age of the SPs can be used to determine the most likely reason for tooth loss.
The specific codes for primary teeth are listed below:
D = Sound primary (deciduous) tooth
K = Primary tooth with surface condition
Note again if both a permanent and a primary tooth are visible in the same tooth space, only the status of the permanent tooth is described and no score is assigned for the primary tooth.
General Guidelines for Scoring
The tooth and surface codes are listed again here for convenience. They are as follows:
Tooth Codes
S = Sound permanent tooth (no decay or filling on any surface)
Z = Permanent tooth with surface condition
D = Sound primary (deciduous) tooth
K = Primary tooth with surface condition
U = Unerupted tooth
E = Missing due to dental disease (caries/periodontal disease)
M = Missing due to other causes (orthodontic/traumatic or other non-disease)
R = Missing due to dental disease but replaced by a fixed restoration
X = Missing due to other causes but replaced by a fixed restoration
P = Missing due to dental disease but replaced by a removable restoration
Q = Missing due to other causes but replaced by a removable restoration
J = Permanent root tip is present but no restorative replacement is present
T = Permanent root tip is present but a restorative replacement is present
Y = Tooth present, condition cannot be assessed
Surface Codes
For caries, the allowable codes are as follows:
0 = Lingual caries
1 = Occlusal caries
2 = Facial caries
3 = Mesial caries
4 = Distal caries
For filled teeth or restoration, the allowable surface codes are as follows:
5 = Lingual restoration
6 = Occlusal restoration
7 = Facial restoration
8 = Mesial restoration
9 = Distal restoration
C = Crown (short call for both primary and permanent teeth)
Recording Procedures
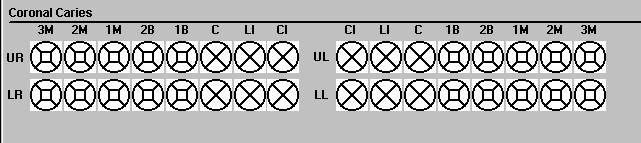
The Coronal Caries screen is divided into four rows, which correspond to the four quadrants of the mouth: upper right, upper left, lower left, and lower right. These quadrants are labeled on the left portion of the screen. The teeth are labeled across the top. Space to enter the overall caries tooth call and the individual surfaces caries is provided for each tooth except the third molars. There is space to enter codes for seven teeth per quadrant. No more than 28 permanent teeth can be scored for each SP. Third molars, or wisdom teeth, are not scored for dental caries.
NOTE: The examiner and recorder are both responsible for making sure that the calls the examiner makes are being recorded in the correct tooth space. In order to do this consistently, each tooth position is to be referred to by its quadrant location and tooth location. For example, whenever a new quadrant is started or there is a long silence between calls, the recorder will prompt the examiner with the next blank tooth space, such as “upper left central incisor”.
The following conventions have been adopted in the interest of achieving diagnostic consistency:
1. Only one entry can be made for each tooth surface. In the event that a surface has both decay and a filling, only the decay is called. If the examiner gives two calls for the same surface, the recorder should bring this to the examiner’s attention immediately.
2. If a tooth has rotated, surface calls should be assigned to the anatomical surface not to the current position of the surface.
3. Incisal edges of anterior teeth are not considered to be separate surfaces. If a lesion or restoration is confined solely to the incisal edge, its score should be assigned to the nearest adjacent surface. If the lesion is equidistant from the surfaces, code lingual.
4. Anterior teeth have four surfaces that are coded – facial, lingual, mesial, and distal.
5. Posterior teeth have five surfaces that are coded – facial, lingual, mesial, distal, and occlusal.
6. When a caries lesion (not filled) extends beyond the line angle onto another surface, that surface is also scored as carious. For restorations, however, the following rules apply:
- On anterior teeth, a proximal filling is not considered to involve the adjacent facial or lingual surface unless it extends at least one-third of the distance onto the adjacent surface. The reason for this criterion is that some of the tooth structure on facial or lingual surfaces of anterior teeth must often be removed to provide access for the proximal restoration, even if there is no decay on the facial or lingual.
- On posterior teeth, to guard against a similar possibility of overcalling, a proximal restoration should extend more than a millimeter past the line angle before it is considered to involve the adjacent facial or lingual surface.
7. If a tooth has a full crown restoration placed because of caries, the tooth will be coded as “C,” which represents the maximum number of surfaces for the tooth type, i.e., four surfaces on anterior teeth and five surfaces on posterior teeth.
The following conventions apply:
- All full crowns on posterior teeth, including abutment teeth for fixed or removable prostheses, will be considered to have been placed due to caries.
- On anterior teeth, however, the examiner should make a determination of the reason for crown placement. If it can be determined that the crown was placed solely for a reason other than caries, such as fracture, malformation, esthetic dentistry, or bridge abutment, the tooth is coded “Y.”
For three-quarter crowns, the following rules apply:
- In general, if a tooth has been restored with less than full coverage, each surface is examined and scored in the usual manner. However, when the crown coverage extends onto the facial (labial or buccal) or lingual surface for cusp protection, the surface is not scored as restored unless the coverage extends more than two millimeters cervically from the cusp tip or incisal edge.
- For three-quarter crowns used as abutment teeth, all surfaces are scored in the usual manner if the abutment is a posterior tooth. On anterior teeth, if it can be determined that the crown was placed solely for purposes of abutment and not for caries, the restorations is not scored, but surfaces without crown coverage are examined and scored in the usual manner.
8. Teeth that are banded or bracketed for orthodontic treatment are examined in the usual manner and all visible surfaces are scored.
9. Certain teeth, notably first bicuspids, may have been extracted as part of orthodontic treatment. These teeth are coded “missing due to other causes”, “M”, and will be excluded from the DMFS analysis. The examiner must make the determination that the teeth were in fact extracted for orthodontic reasons. This is usually not difficult to determine because of the typically symmetric pattern of these extractions. For the sake of uniformity, all orthodontically extracted bicuspids are scored as first bicuspids. Teeth other than bicuspids may also be extracted for orthodontic reasons. In many cases the SP will have good recall of the reason for the extractions and can help in making the correct determination.
10. Nonvital teeth are scored in the same manner as vital teeth. If, however, a restoration on a nonvital tooth was placed solely to seal a root canal and not for caries, that restoration is not scored. If no other lesions or restorations are present, the tooth will be called sound (“S”).
11. Hypoplastic teeth are scored in the usual manner. However, if it can be determined that a restoration was placed solely for esthetic reasons and not for caries, that restoration is not scored. If a hypoplastic tooth is restored with a full crown, it is to be coded “Y”.
12. Malformed teeth are scored in the usual manner, except when they have been restored with a full crown for esthetic reasons, in which case they are coded “Y”.
13. When the primary tooth crown is destroyed by caries and only the roots remain, score all surfaces carious (5 surfaces on the posterior teeth – 0, 1, 2, 3, 4; and 4 surfaces on the anterior teeth – 0, 2, 3, 4).
14. When the same tooth surface is both carious and filled, only the caries is scored.
15. Fractured or missing restorations are scored as if the restoration was intact unless caries is found to be present. In that case, the involved surface is scored as carious rather than restored.
16. In the case of supernumerary teeth, only one tooth is scored for the tooth space. The examiner must decide which tooth is the “legitimate” occupant of the space.
17. If both a deciduous and a permanent tooth occupy the same tooth space, only the permanent tooth is scored.
18. Third molars are not scored. When examining second molars, it is important to note that a drifted third molar may occupy the space of a missing second molar. In such cases, the diagnosis and score must relate to the status of the missing second molar, not the third molar. If the second molar, for example, was extracted due to caries and a sound third molar now occupies the space, the second molar is scored as extracted (“E”) and the third molar is not scored.
19. A tooth is considered to be in eruption when any part of its crown projects through the gum. This criterion is easier to standardize than one based on a more advanced stage of eruption.
20. Stain and pigmentation alone should not be regarded as evidence of caries, as either can occur on sound teeth.
If the tooth is permanent with no decay or filling on any surface, the examiner calls “S.” If the tooth is permanent and is not sound, the examiner calls “Z” and the appropriate surface condition codes as described below. “D” is entered for all sound primary calls while “K” and the appropriate surface condition codes are entered if the primary tooth has surface conditions (caries, restoration). If the tooth is missing and characterized by one of the other “tooth” calls, the examiner calls out the appropriate letter (U, E, M, R, X, P, or Q).
The recorder records the appropriate tooth condition code in the first space for the tooth. After this first space, there is a separate block of data entry spaces to accommodate the surface calls for that tooth, as necessary.
If the tooth is permanent with decay or restorations on one or more surfaces (Z), the examiner calls the number(s) which correspond(s) to the surface(s) having decay or a restoration. Some examples are listed below.
- If the examiner calls 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4, it means that there is decay on the surfaces of the tooth represented by those numbers.
- If the examiner calls 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9, it means that there is a filling on the surface(s) represented by the number(s) called.
- If the examiner calls “C,” it means that there is a crown on that tooth.
- Combinations of caries and restorations on different surfaces are allowed. For example, if the examiner calls “1, 8, 9” it means that there is caries on the occlusal surface and a restoration on the mesial and distal surfaces.
This procedure continues to the second molar for each of the four quadrants of the mouth.
Personnel and Training Required
A dentist or dental hygienist conducts the dental exam and calls the results to a health technician who records the findings.
Equipment Needs
No. 3 plain mirror and an explorer. The health technician can record the examiner calls on a paper form or can use a computer data entry system that would require a laptop or desktop computer.
Requirements
| Requirement Category | Required |
|---|---|
| Major equipment | No |
| Specialized training | Yes |
| Specialized requirements for biospecimen collection | No |
| Average time of greater than 15 minutes in an unaffected individual | No |
Mode of Administration
Clinical Examination
Lifestage
Child
Participants
Participant ≥6 years of age
Selection Rationale
This clinical examination is taken from a national study.
Language
Chinese, English
Standards
| Standard | Name | ID | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) | Oral dental caries proto | 62582-2 | LOINC |
| Human Phenotype Ontology | Carious teeth | HP:0000670 | HPO |
| caDSR Form | PhenX PX080301 - Dental Caries Experience Prevalence | 5965098 | caDSR Form |
Derived Variables
None
Process and Review
Not applicable.
Protocol Name from Source
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth Surfaces (DMFS) Index, 2003-2004
Source
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). 2003–2004. Dental Examiners Procedures Manual, Section 4.9.1.3.General References
None
Protocol ID
80301
Variables
Export Variables| Variable Name | Variable ID | Variable Description | dbGaP Mapping | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL1B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301250100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL1B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301250200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL1M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301230100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL1M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301230200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL2B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301240100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL2B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301240200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL2M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301220100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LL2M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301220200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLCI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301280100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLCI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301280200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLC_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301260100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLC_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301260200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLLI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301270100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LLLI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301270200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR1B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301110100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR1B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301110200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR1M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301090100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR1M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301090200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR2B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301100100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR2B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301100200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR2M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301080100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LR2M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301080200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRCI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301140100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRCI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301140200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRC_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301120100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRC_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301120200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRLI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301130100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_LRLI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301130200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL1B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301180100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL1B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301180200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL1M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301160100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL1M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301160200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL2B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301170100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL2B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301170200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL2M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301150100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UL2M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301150200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULCI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301210100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULCI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301210200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULC_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301190100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULC_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301190200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULLI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301200100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_ULLI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301200200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR1B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301040100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR1B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301040200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR1M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301020100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR1M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301020200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR2B_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301030100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR2B_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301030200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR2M_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301010100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_UR2M_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301010200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URCI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301070100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URCI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301070200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URC_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301050100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URC_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301050200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URLI_Tooth_Code | ||||
| PX080301060100 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
| PX080301_DMF_Index_URLI_Tooth_Surface | ||||
| PX080301060200 | The Decayed, Missing, or Filled Tooth more | N/A | ||
Measure Name
Dental Caries Experience - Prevalence
Release Date
December 30, 2009
Definition
A measure to assess the Decayed, Missing or Filled Tooth Surfaces.
Purpose
To determine the prevalence of coronal caries in primary (deciduous) and permanent teeth and to record the presence of treated (filled) or missing teeth. The resulting score is an indicator of the health status of the individual's teeth.
Keywords
Oral health, Teeth, Tooth decay, Missing teeth, Filled teeth, Treated teeth, Clinical examination, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Dental caries, Coronal Caries
Measure Protocols
| Protocol ID | Protocol Name |
|---|---|
| 80301 | Dental Caries Experience - Prevalence |